I just finshed reading Rocket Surgery Made Easy. As the title so clearly says it is a do-it-yourself guide to finding and fixing usability problems.
The author´s name is Steve Krug and here´s what he looks like according to the book.  So next time you happen to be at a usability conference make sure you say hello...
So next time you happen to be at a usability conference make sure you say hello...
My current personal goal is to become really good at usability testing so I try to read good books and browse the web for videos, talks and other useful stuff like templates for creating prototypes. This post will focus on my interpretation of what Steve says.
Have You Ever Met a Good Midget Comedian?
This book is just like a really good midget comedian... very short and very funny. It is full of headlines like this one together with those nerdy quotes that we all love to hate and cherish so much. The title may as well have been Usability testing made entertaining. For a long time I tried to make usability a part of the IT-projects I worked in with limited success until I decided to keep it very simple and do it myself. If there is something I have learned from 20 years in business it is that large, complicate and cumbersome stuff never ever gets done! At least not for real or for very long.
In my opinion, the essence of the book is:
"Let´s make it so easy and still so rewarding that it´s very hard to motivate not doing it!"
Even better, the book in itself is made accessible so there is hope that even the most reluctant readers can get through it. To be really clear, this is a book on how to get you STARTED, not the comprehensive works that can be found elsewhere. The problem with most thicker books is that usually at least half of the words are totally unnecessary making the reading experience not very pleasant and then there is so much information that it is really hard to find out what is most important. So cudos for effectively distilling usability into something more devourable.
So by now you have realised that I really liked this book! I like it so much that I will most likely use it as course litterature for a one day usablity class I am planning to create. I would love to translate it to Swedish to make it even more accessible fo my fellow countrymen.

The Core Process of Usability Testing
Let us start with the goal of usability testing made easy:
Our goal is to find and fix the most serious problems in order to make products easier to use.
That´s really all there is to it. We don´t try to find all of the problems and we do not bother about statistical significance in our measurements. The point is that bad usablity shows itself readily and even if we found momore problems, there would be no time to fix them. So if we can find what is hurting the most and fix this right away, we stand a great chance to end up with a great product. This type of usability testing has one large advantage over more advanced versions - this one get´s done(hopefully)!
If you look at the tis on planning and execution it is pretty clear that this is usability the agile way - and agile is good for us, right?
When Do We Start
"Start earlier than you think makes sense" (S Krug)
Right along the lines with Lean UX we start testing early and continue throughout the project. We have a hypothesis and we test it to see how well it works. How? Create a prototype and do a usability test. It is soooo easy to create a prototype in powerpoint or Omnigraffle that it is criminal not doing it! It saves so much time if we test before the developers have started coding. Of course we need to do some background work beforehand mapping the user experience or creating an impact map so we understand what the real problem is. This is not discussed in detail in this book but an earlier blog post. is a good start for learning more.
One Hour Well Spent
A test session takes only one hour, an extra half hour extension is possible but in my experience that may be too long both for booking people and for keeping focus.. Make sure that everything is well prepared. Since we have only one hour to spend, there is no time for last minute fixes like not having your test data or equipment ready. The easiest possible configuration is to have a device with your application loaded, and one test manager telling the participant what to do and then observing and taking notes. The recommendation is to have at least one observer - in the same room if you can keep them from talking during the test. I find it a bit hard to take great notes at the same time as I am leading the test.
Now here is an important point that Steve makes. Having more observers gives us many advantages:
- people make different observations
- it is a great learning experience for everyone involved
- it helps getting team consensus on what to fix
- the understanding for why usability testing is needed increases
These additional observers should be kept in another room since too many people in the same room make he subject feeling watched - which is a correct observation - and that will disturb the testing. So hook up a big screen using GoToMeeting or any other tool you have - Skype or Project Place can work although I have found Skype a bit choppy at times. Use an external microphone and extra speakers to record and replay the talk aloud and instructions. No need to record the face of the tester - audio is enough. Recors the screen if you think there is actually a chance that you will watch the re-run. It can of course be good ammunition for pointing out a problem later.
Now introduce the tester to what they will do and make sure they understand we are testing to see if OUR DESIGN HAS PROBLEMS not if they are skilled! Don´t forget this and don´t tell them more than three times in a session since this will lead them to think the opposite.
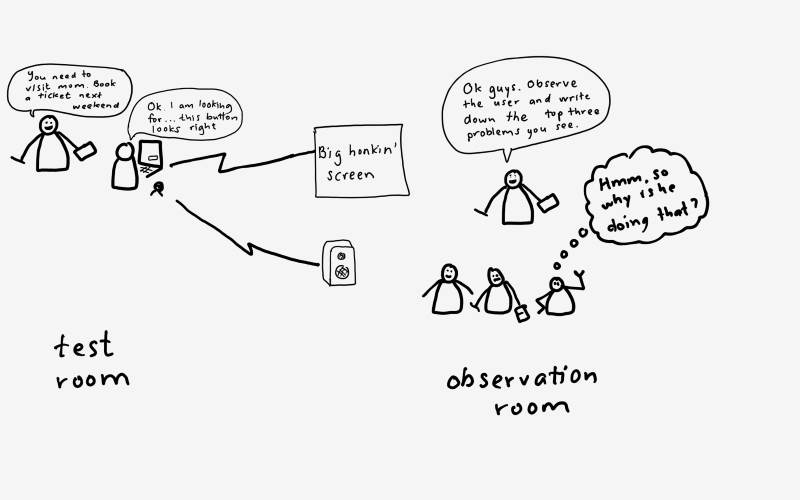
Now it is great to have another test lead in the observation room to distribute the tasks in written format together wih a place where the observers can write what they see and sum it up in their top three problems.
Post Test Session Processing
Meet with all of the observers. Collect all top three observations. I like to do this on post-its. Do a collective sorting and prioritising. And voila, you have a list of most important things to fix and some other stuff that you will not fix right now. It may seem a bit provocative to some - but if you have not observed - you don´t get to vote. Cause we are not voting on what you think is bad - we make the prioritisation on what you actually observed! This will hopefully make more people wanting to observe. Time well spent I think!
So that´s it. No big report that noone will read, no huge list of to do that we have no chance getting done. Pretty agile, huh!
Final Words
Last project I worked in failed miserably at the usabilty testing part. Lack of understanding and knowledge was the biggest culprit. If was to take the advice from Steve I would have run tests from early on although the web interface looked crappy for a very long time. I would have created a quick prototype on my own to start with just to have something that enabled me to get feedback. I would also have used my colleagues and friends as testers since many usability problems have to do with general things like navigation and information that also non-business specialist will run into. I would have recorded sessions and shown them to the members of the project.
I was so pleased after reading this book that I bought and read the updated version of Don't make me think. This is a good read as well but more about that later...